Putting User Needs Mapping into practice
When you’re ready to move from insight to action, UNM provides a structured yet adaptable process to map how user needs flow into work, capabilities, teams and value. Whether you’re new to User Needs Mapping or ready to apply it, this page walks you through the core steps and how they fit together.
Step 1: Define the purpose
Begin by clarifying what you’re trying to achieve with this mapping session.
What user-outcome are you aiming to improve?
Which part of the organisation (product, service, value stream) will you explore?
What questions about alignment, dependencies or team interactions do you want to answer?
Setting a clear purpose helps focus the session and ensures participants stay aligned.
Step 2: Identify the user(s)
Choose the user or user-group whose needs matter for this context: external customers, internal stakeholders, or value-consumers.
For each user, articulate a simple outcome-statement – what they’re trying to achieve, how they feel, and the context.
Example: “When I want to choose and book a film, I want a seamless experience so that I feel confident and relaxed.”
Step 3: Define user needs
Translate user outcomes into outcome-focused needs (not tasks or features).
Ask: What progress is this user trying to make?
Collect a set of needs for your user, then prioritise or cluster them.
This step helps move from inside-out thinking (“we will build X”) to outside-in (“what does the user need?”)
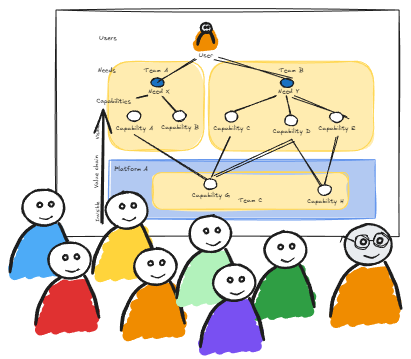
Step 4: Map capabilities
For each user need, identify the organisational capabilities required to fulfil it. Capabilities may include systems, processes, teams, skills or services. You’re building a chain from need → capability. This reveals where your organisation is structured (or not) to meet those needs.
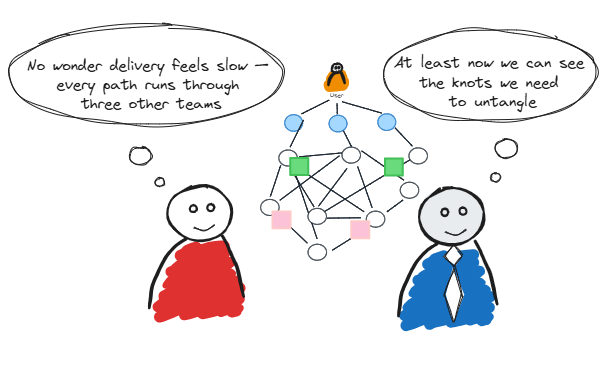
Step 5: Analyse dependencies
Look for insights based on the map you have produced: where one capability relies on another; where teams hand off; where systems integrate. Dependencies aren’t bad in themselves, but when they obstruct flow, create delays, or introduce cognitive load, they become friction. Look for clusters of dependencies, overloaded teams, or unclear hand-off points.
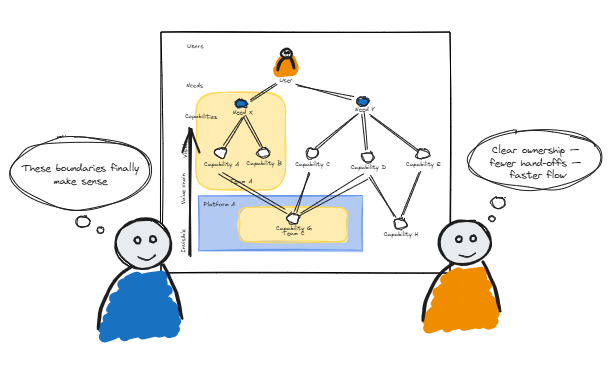
Step 6: Define team boundaries & interactions
Now you shift focus: given the capabilities and dependencies mapped, consider team boundaries, ownership and interaction modes. Ask:
Which team should own which capability?
Are hand-offs creating cognitive load or structural delay?
Could a boundary be redesigned to reduce friction?
User Needs Mapping makes visible how teams should interact, rather than simply how they currently do.
Step 7: Iterate and scale
UNM isn’t a one-off exercise. Use the map as a living artefact.
Revisit it when new user needs emerge.
Add new capabilities, highlight new dependencies.
Adjust team boundaries and interaction modes as the context evolves.
Small, incremental changes are more sustainable than sweeping reorganisations.
Why this process matters
By walking through needs → capabilities → dependencies → teams → flow, you shift from building inside → out from your organisation’s structure, to designing outside → in from user value. The map gives you a shared visual language across product, engineering, delivery and leadership, making structural misalignment visible and actionable.
Practitioner tips
Keep sessions manageable: focus on one user and a handful of needs initially, then expand.
Use sticky notes or digital boards to make the map tangible and collaborative.
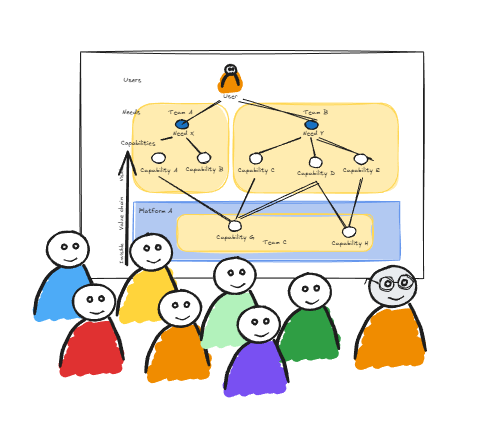
Involve a cross-functional group: product, engineering, operations, key stakeholders.
Use the map to ask “why?” at each level — Why this capability? Why this ownership?
Don’t aim for perfect first time: iterate, learn, refine.
Your next move
Ready to try User Needs Mapping in your team? Start by selecting your user journey and mapping three user needs. Then map the capabilities and dependencies. Use what you discover to prompt a conversation about how your team boundaries and interactions might evolve for better flow.
And you don’t have to figure it out alone; I work with teams to run mapping sessions, build confidence in applying the approach, and turn insights into structural clarity. Get in touch to explore how I can support you.
Tailored User Needs Mapping workshops where we’ll uncover misalignment, clarify capabilities, and identify practical flow-improving moves grounded in your real context.
If you need more, I can partner directly with you to help evolve team boundaries, reduce friction, and build fast-flow ways of working over time.
Walk through an example to better understand the thinking and benefits behind User Needs Mapping